1
/
of
3
Douglas Labs
Douglas Laboratories B6-100mg
Douglas Laboratories B6-100mg
Regular price
$ 12.99 USD
Regular price
$ 18.99 USD
Sale price
$ 12.99 USD
Unit price
/
per
Couldn't load pickup availability
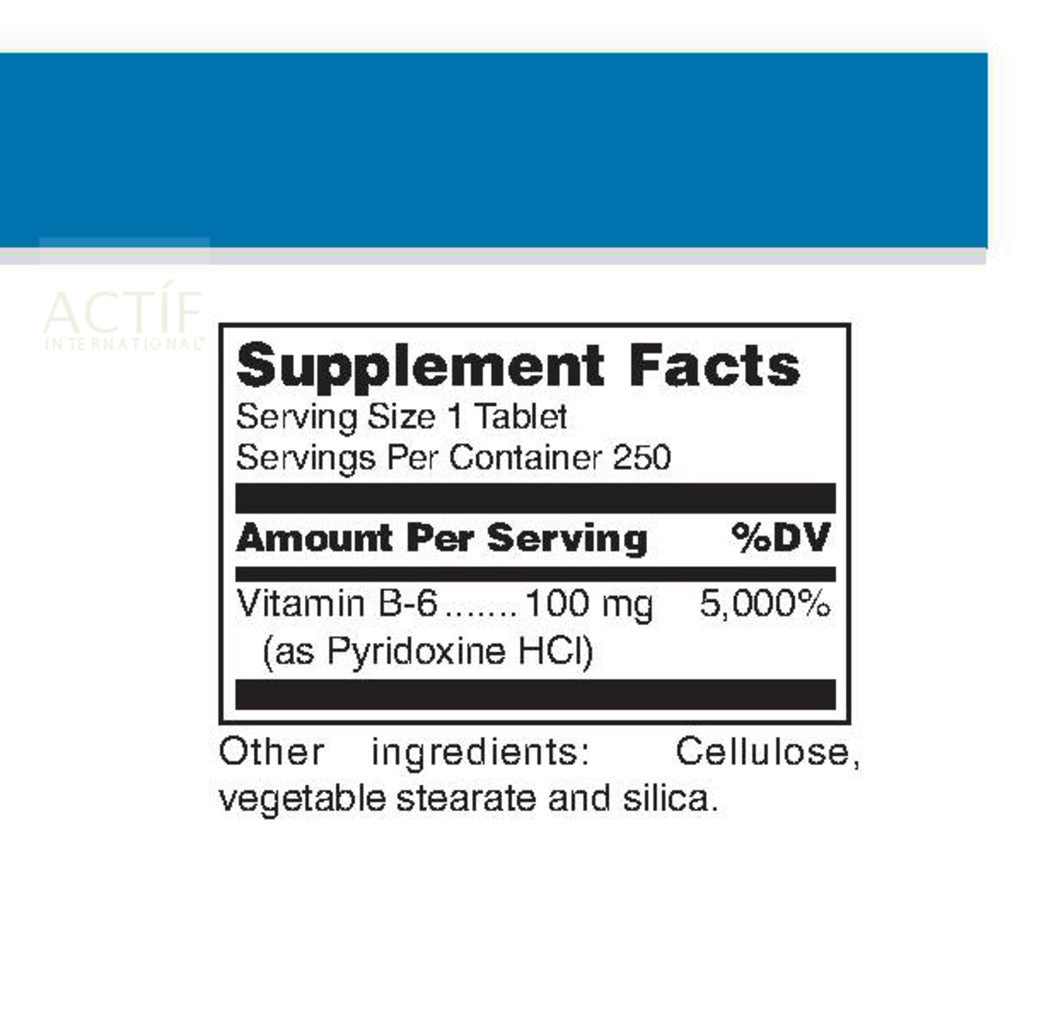
100 mg of Vitamin B in each tablet.
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and other nitrogen compounds. In the liver, pyridoxine is essential for glucose production from amino acids via its role as a coenzyme for the transaminase enzymes. Pyridoxine is also needed by the liver and muscles to make stored glycogen available for glucose production, and to synthesize niacin from the amino acid tryptophan.
In the nervous system, pyridoxine is needed to synthesize several neurotransmitters, such as serotonin (from tryptophan), taurine, dopamine, nor-epinephrine, histamine and gammaaminobutyric acid. It also regulated oxygen in the red blood cells.
Suggested Dosage: Adults take 1 tablet daily.
Share